Modernize to cloud, and on cloud
Cloud migration has been a major trend in the past years. “Lift & Shift” migrations allowed organizations to rapidly benefit from cloud infrastructure capabilities with minimal disruption and effective costs.
However, rehosted applications may not leverage all powerful capabilities of cloud-native services including high performance, automated scalability, security, resiliency or more advanced services such as modern databases, analytics and AI.
In fact, only a fraction of applications have been migrated to the cloud. Applications still on premises are typically the most complex or monolithic stacks, developed over the years by changing development teams, with limited documentation, where rearchitecting or heavy refactoring is necessary before considering a cloud migration. Before engaging in such endeavour, organizations need to make sure that the technical knowledge base of those applications is available.
How CAST can help
The journey begins with CAST Highlight (covered in another workshop) with which, in a week, organizations can scan the source code of hundreds of custom applications which get automatically categorized according to the Gartner 5Rs (Rehost, Refactor, Rearchitect, Rebuild and Retire), with a list of cloud blockers and remediation effort estimates, recommended AWS services, opensource risks (CVEs, obsolescence and copyleft license risks, SBOM).
Then, when Modernizing to Cloud and on Cloud, CAST Imaging is crucial for critical applications in Rearchitect or Refactor scenarios to:
-
Rapidly understand the AS-IS structure of an application
-
Identify the transformation hurdles in the code
-
Plan and estimate the impact of the modernization scenarios such as fixing a Cloud blocker, integrating an AWS Service or carving out a legacy portion of the code and create new bridges, etc.
-
Centralize the technical knowledge and share the vision with the rest of the team
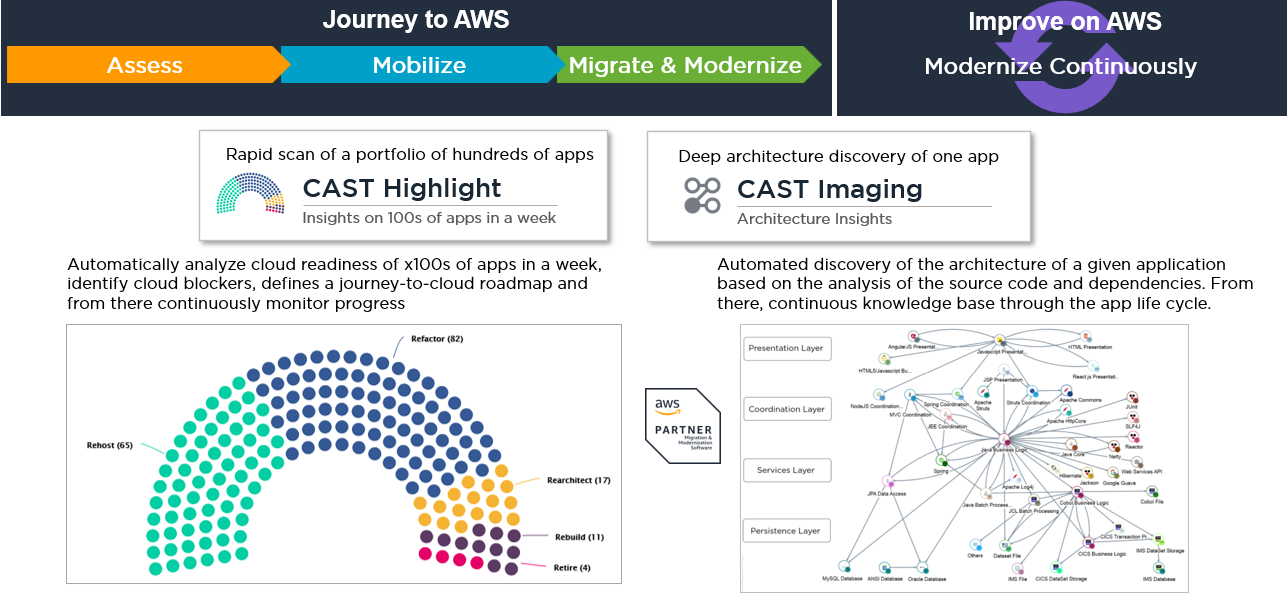
Beyond the initial assessment, CAST Imaging is used for continuous monitoring of the journey-to-cloud program and to secure the natural evolution of your custom applications by providing an up-to-date technical knowledge base of the application code.